Ferry Ath Thaariq Mudhofir

A dedicated junior geophysicist and data enthusiast with hands-on experience in subsurface exploration and data-driven decision-making. Keen to contribute to innovative projects that foster creativity.
"Numbers have important stories to tell, data will speak if you’re willing to listen."
Portfolio
Data Science
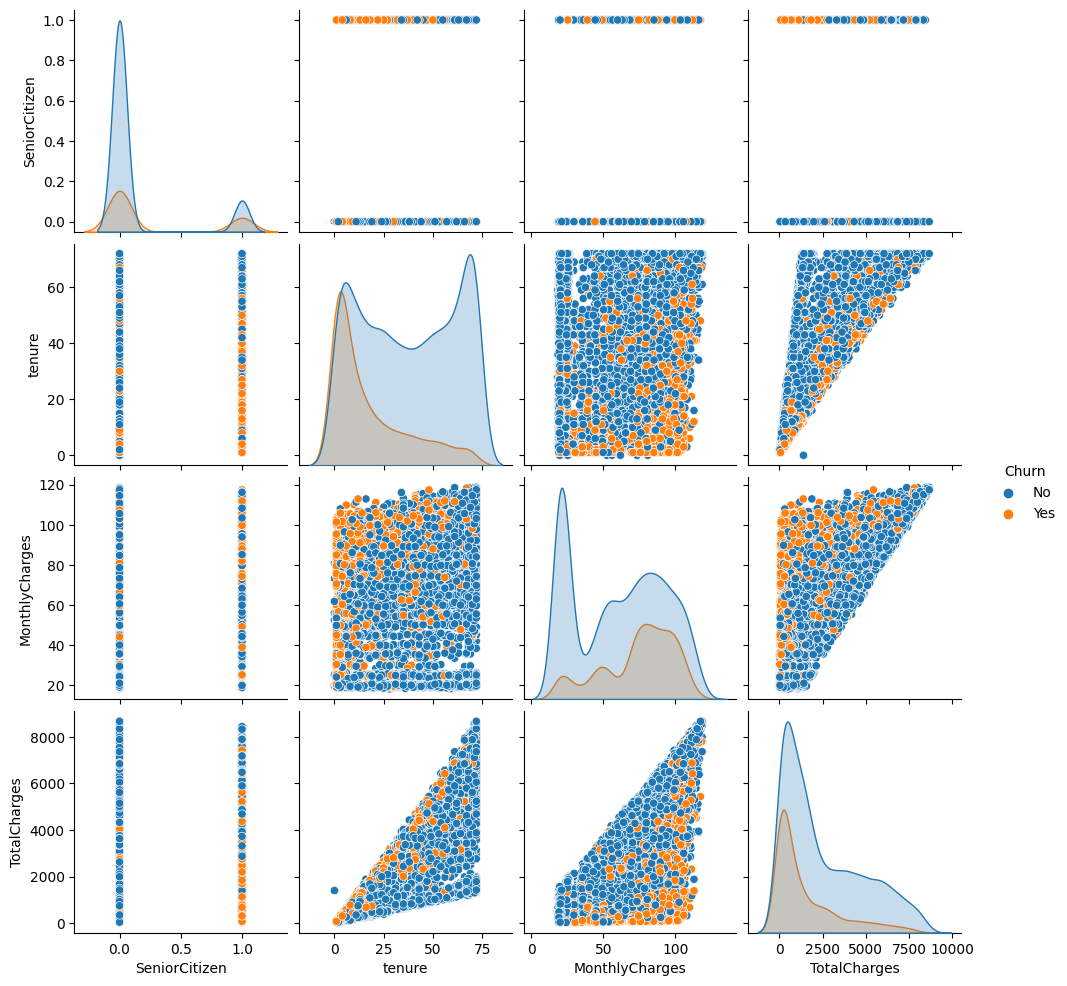
Exploratory Data Analysis: Uncovering Patterns Behind Telco Customer Churn
Through an in-depth analysis of churned customer data, we successfully identified the profiles of customers more likely to leave the service, the key factors influencing churn decisions, and also the critical moments when customers are most likely to discontinue their subscriptions. These findings can be leveraged to develop more effective retention strategies.
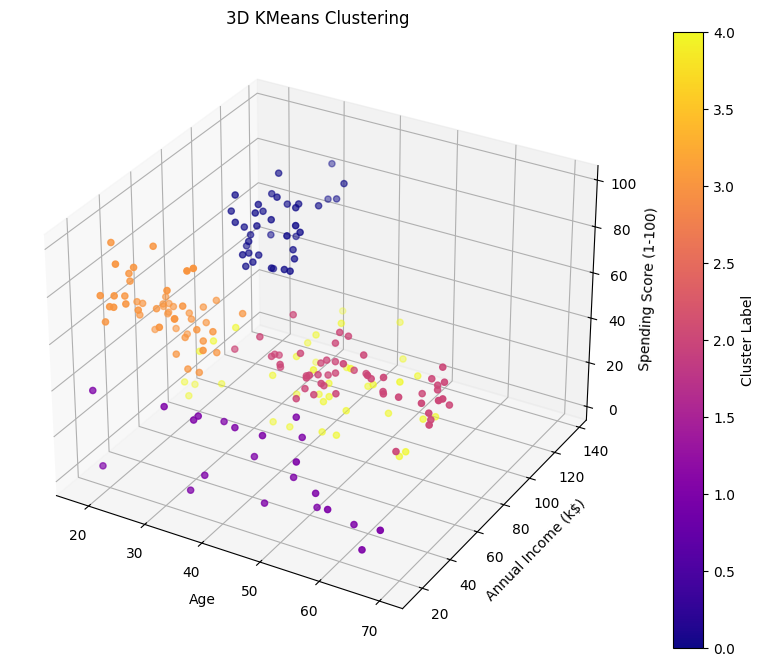
Mall Customer Segmentation Using KMeans Clustering
This project focuses on applying KMeans Clustering to analyze customer data from a mall. The objective is to identify consumption patterns and customer segmentation based on data such as age, annual income, and spending score. This data-driven approach produces customer groups that can be leveraged to support business strategies.
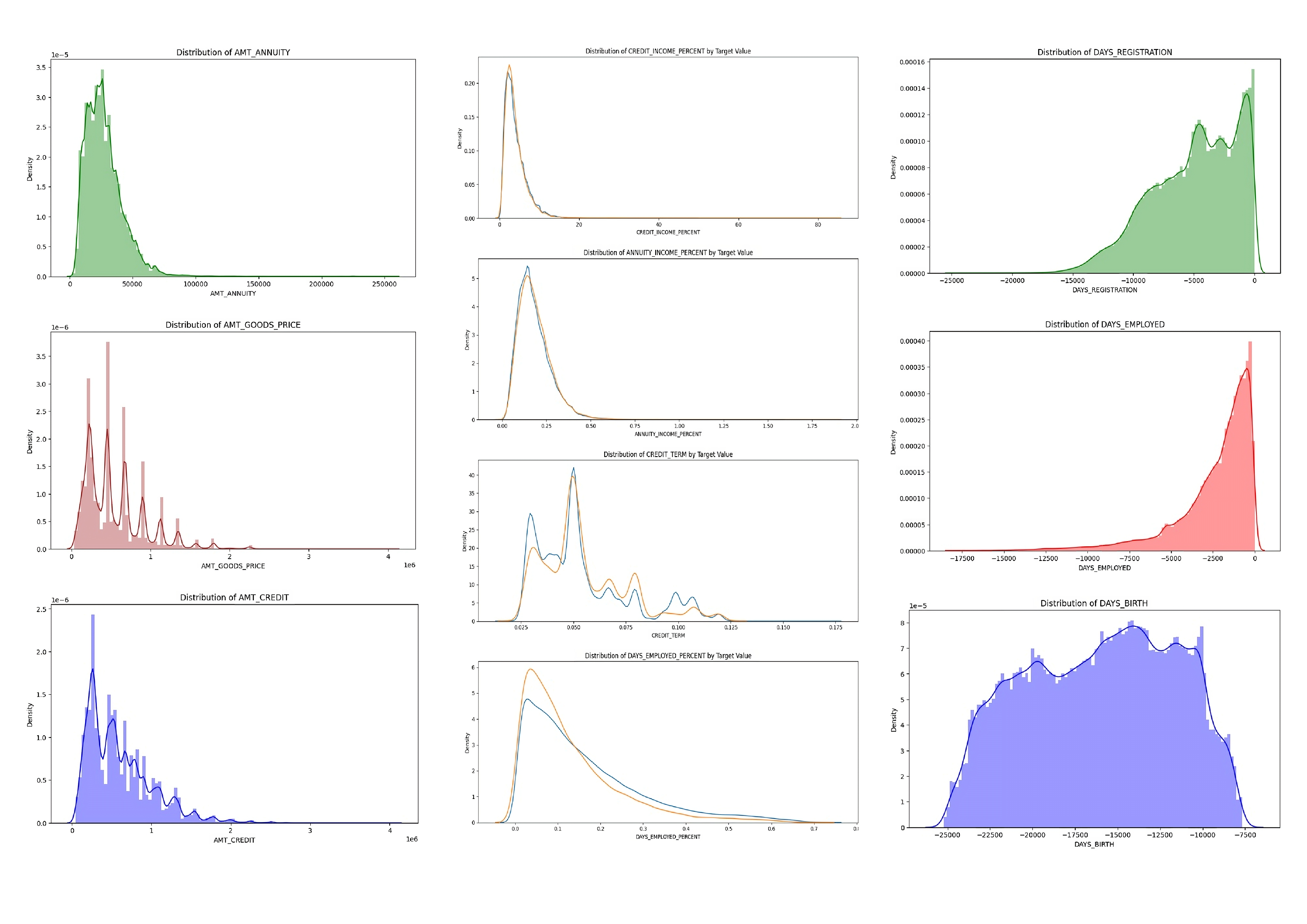
Customer Churn Prediction on Home Credit Default Risk
This project utilized the Home Credit Default Risk dataset to develop a machine learning-based model for predicting default risk, with imbalanced target data (91.93% vs 8.07%). After imputing missing values, applying one-hot encoding, and creating features, the Random Forest Classifier (RFC) model achieved 87% accuracy and 0.77 AUC-ROC.
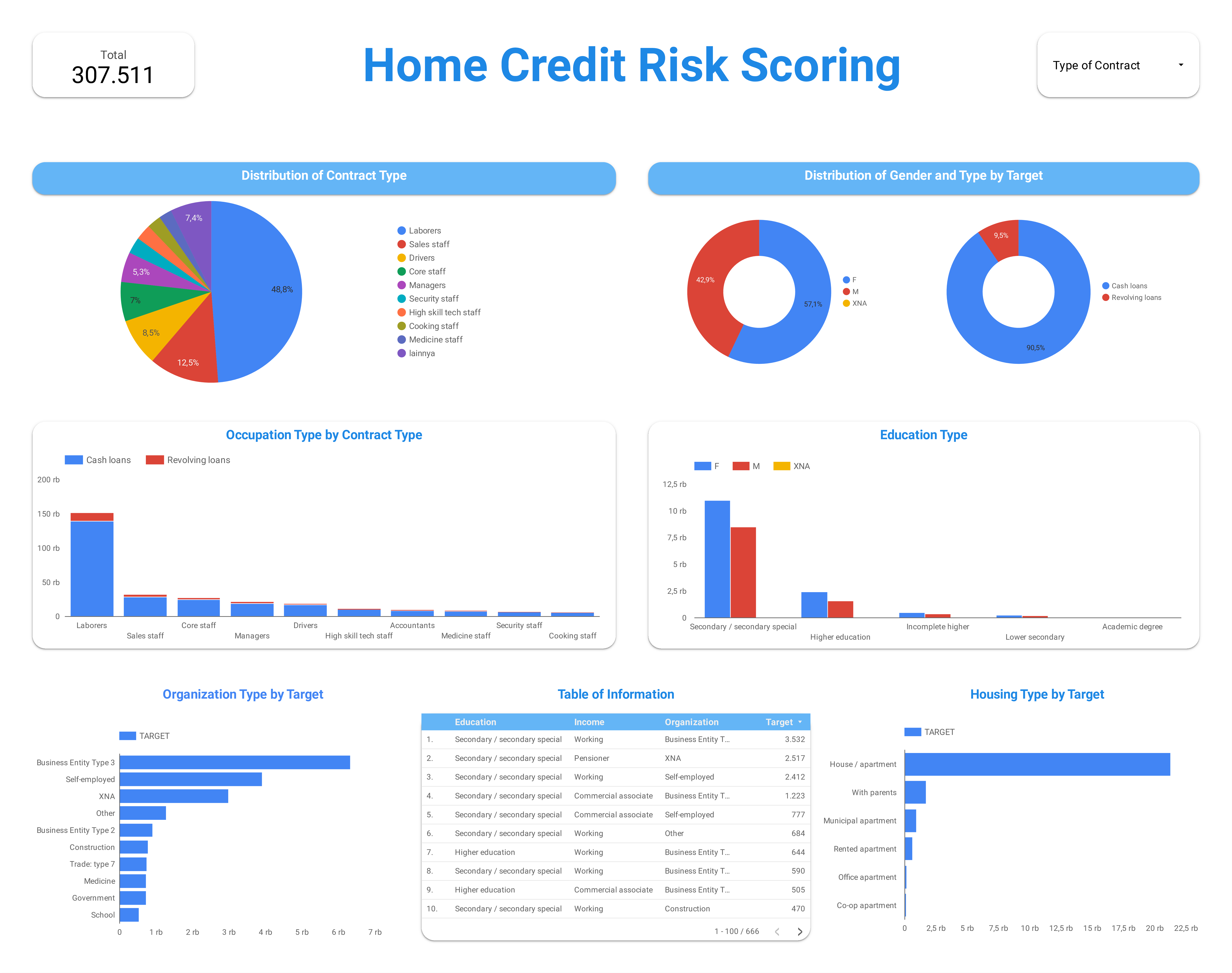
Detikcom in Numbers: Understanding User Preferences
This dashboard allows us to delve deeper into what Detikcom users truly want. Through interactive data visualizations, we can understand reading preferences, identify trends, enhance engagement, analyze the time users spend on various types of content, optimize user experience, and ultimately drive business growth and improve user satisfaction.
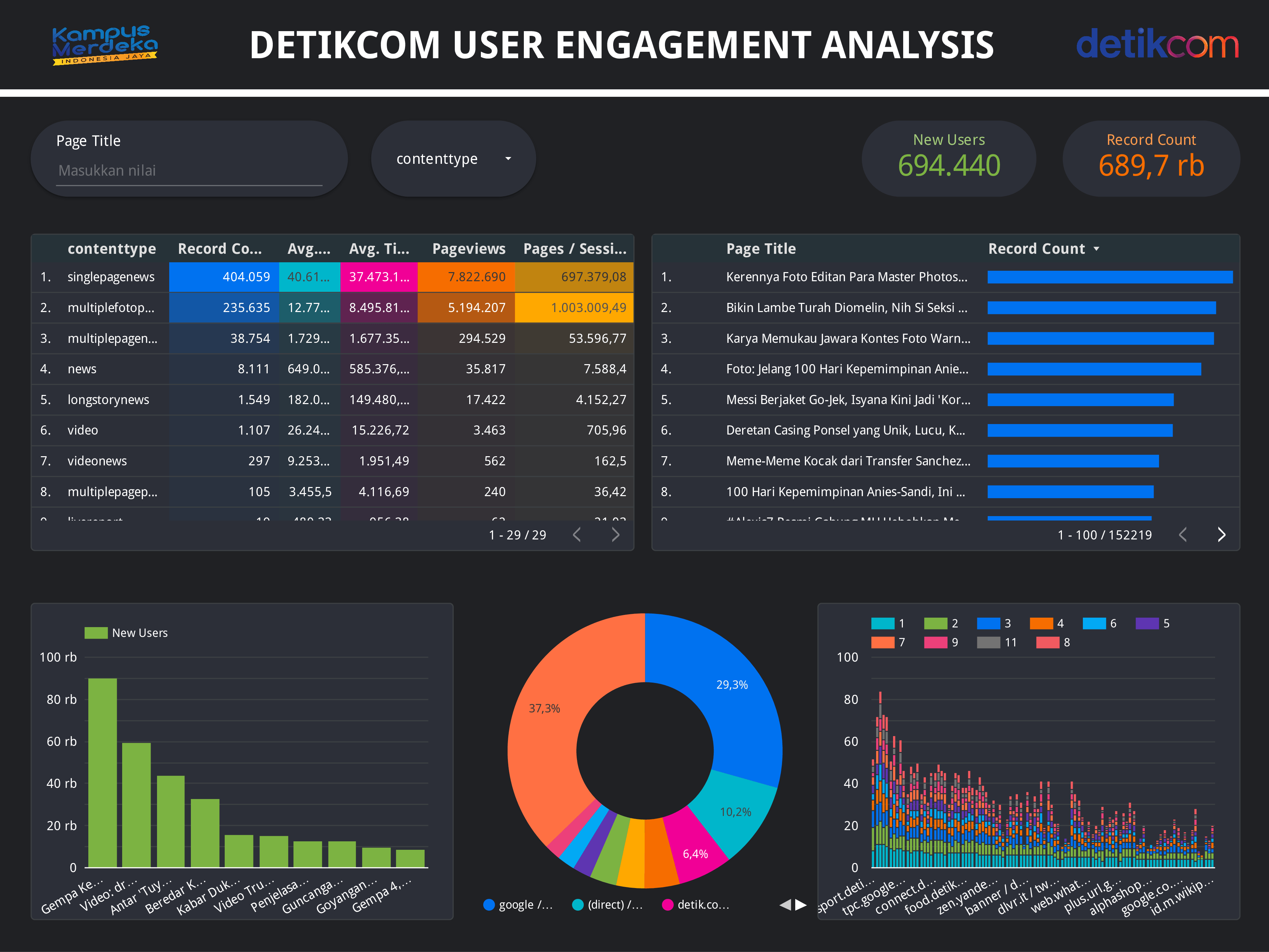
Real-time Forecasting of Global COVID-19 Trends with Random Forest Classifier
Through this project, we developed a Random Forest-based predictive model that accurately projects global COVID-19 case trends using a data-driven approach. The model was evaluated using metrics RMSE and MAE, demonstrating its effectiveness in predicting the number of new cases while identifying regions with potential case surges.
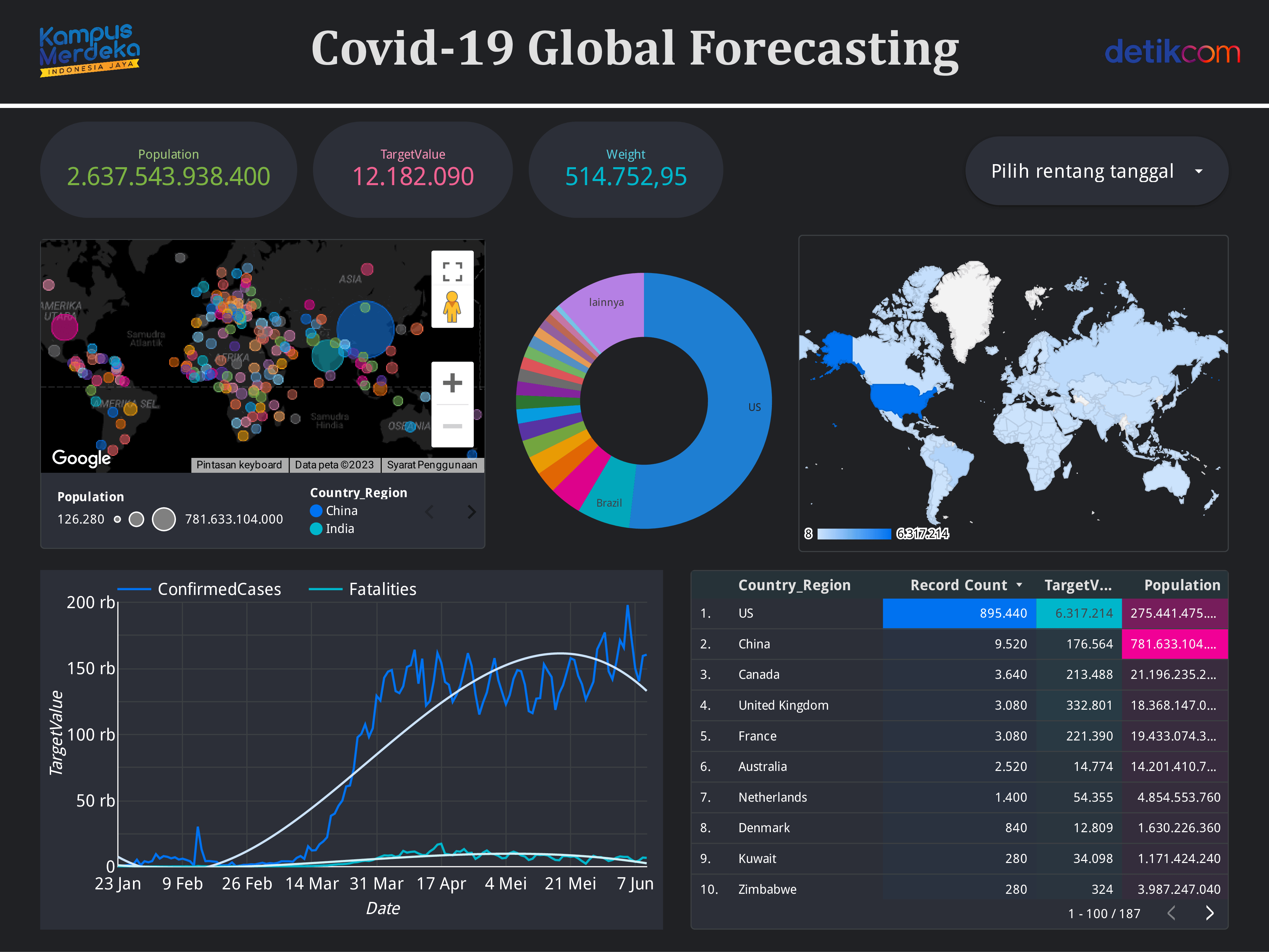
Predict Ames House Prices and Practice Feature Engineering, RFs, and Gradient Boosting
The prediction begins with exploratory data analysis and feature engineering. Random Forest and Gradient Boosting models (XGBoost, LightGBM) are then applied, achieving an RMSE of 0.12 (log-transformed target). Linear Regression and Ridge Regression are used for comparison, with Ridge reducing overfitting and yielding lower errors (MAE, MSE, RMSE). Significant features such as OverallQual, GrLivArea, and GarageCars were identified, providing valuable insights into the factors influencing house prices.
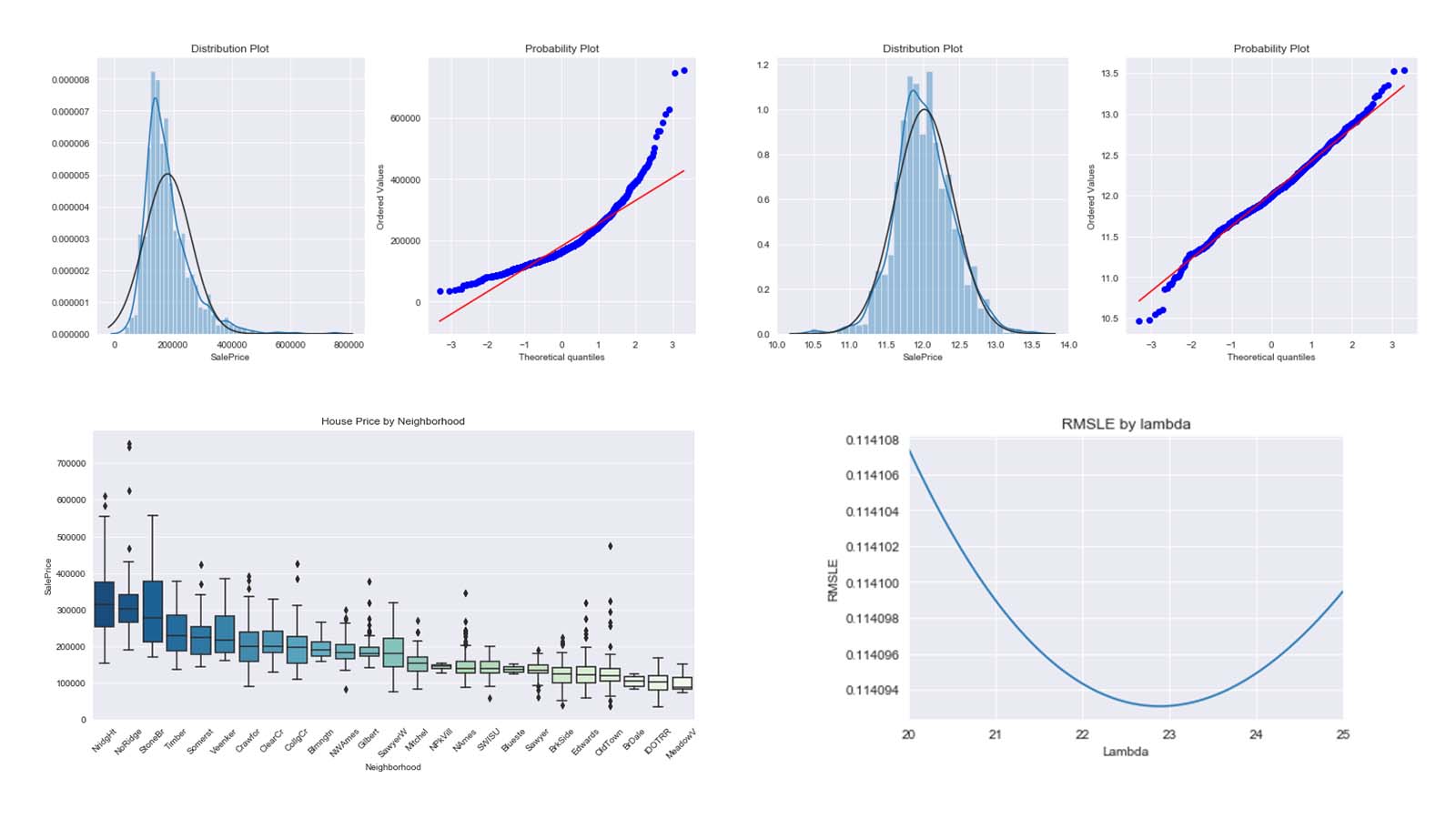
Computational Physics
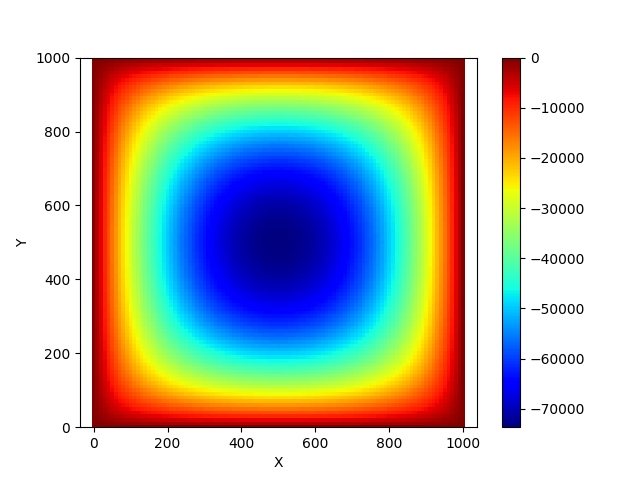
Finite Difference Time Domain
Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) is a numerical method used to solve partial differential equations (PDEs) that describe electromagnetic wave propagation. It is a time-domain approach that discretizes both space and time, representing the fields at each point on a grid and advancing the solution through time using iterative calculations. I have implemented a Python-based Finite Element Method to solve the Laplace equation in a square domain with homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions (the boundary values on each side of the domain zero) using matrix methods.